Introduction to web scraping: XPath Cheatsheet
| Expression | Description |
|---|---|
nodename |
Select all nodes with the name “nodename” |
/ |
A beginning single slash indicates a select from the root node, subsequent slashes indicate selecting a child node from current node |
// |
Select direct and indirect child nodes in the document from the current node - this gives you the ability to “skip levels” |
. |
Select the current context node |
.. |
Select the parent of the context node |
@ |
Select attributes |
text() |
Select the value of an element |
\| |
Pipe chains expressions and brings back results from either expression, think of a set union |
| Operator | Explanation |
|---|---|
= |
Equivalent comparison, can be used for numeric or text values |
!= |
Is not equivalent comparison |
>, >= |
Greater than, greater than or equal to |
<, <= |
Less than, less than or equal to |
or |
Boolean or |
and |
Boolean and |
not |
Boolean not |
Note: Using ‘!=’ is not the same as using ‘not’.
Predicates
| Operator | Explanation |
|---|---|
[1] |
Select the first node |
[last()] |
Select the last node |
[last()-1] |
Select the last but one node (also known as the second last node) |
[position()<3] |
Select the first two nodes, note the first position starts at 1, not = |
[@lang] |
Select nodes that have attribute ‘lang’ |
[@lang='en'] |
Select all the nodes that have a “attribute” attribute with a value of “en” |
[price>15.00] |
Select all nodes that have a price node with a value greater than 15.00 |
Wildcards
XPath wildcards can be used to select unknown XML nodes.
| Wildcard | Description |
|---|---|
* |
Matches any element node |
@* |
Matches any attribute node |
node() |
Matches any node of any kind |
In-text search
XPath can do in-text searching using functions and also supports regex with its matches() function. Note: in-text searching is case-sensitive!
| Path Expression | Result |
|---|---|
//author[contains(.,"Matt")] |
Matches on all author nodes, in current node contains Matt (case-sensitive) |
//author[starts-with(.,"G")] |
Matches on all author nodes, in current node starts with G (case-sensitive) |
//author[ends-with(.,"w")] |
Matches on all author nodes, in current node ends with w (case-sensitive) |
//author[matches(.,"Matt.*")] |
regular expressions match 2.0 |
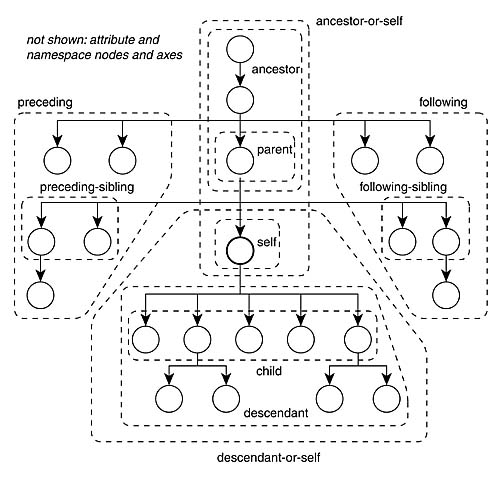
Complete syntax: XPath Axes
XPath Axes fuller syntax of how to use XPath. Provides all of the different ways to specify the path by describing more fully the relationships between nodes and their connections. The XPath specification describes 13 different axes:
- self ‐‐ the context node itself
- child ‐‐ the children of the context node
- descendant ‐‐ all descendants (children+)
- parent ‐‐ the parent (empty if at the root)
- ancestor ‐‐ all ancestors from the parent to the root
- descendant‐or‐self ‐‐ the union of descendant and self • ancestor‐or‐self ‐‐ the union of ancestor and self
- following‐sibling ‐‐ siblings to the right
- preceding‐sibling ‐‐ siblings to the left
- following ‐‐ all following nodes in the document, excluding descendants
- preceding ‐‐ all preceding nodes in the document, excluding ancestors • attribute ‐‐ the attributes of the context node
XPath in Chrome
View > Developer > Javascript Console. In the Console type in: $x(“/xpath/expression/goes/here”)
Examples
HTML View
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>HTML5 Layout</title>
</head>
<body>
<div class="wrapper">
<header>
<h1>Yoko's Kitchen</h1>
<nav>
<ul>
<li>
<a href="home" class="current">home</a>
</li>
<li>
<a href="classes">classes</a>
</li>
<li>
<a href="catering">catering</a>
</li>
<li>
<a href="about">about</a>
</li>
<li>
<a href="contact">contact</a>
</li>
</ul>
</nav>
</header>
<section class="courses">
<a href="introduction.html">
<article>
<figure>
<img src="images/bok-choi.jpg" alt="Bok Choi" />
<figcaption>Bok Choi</figcaption>
</figure>
<hgroup>
<h2>Japanese Vegetarian</h2>
<h3>Five week course in London</h3>
</hgroup>
<p>A five week introduction to traditional Japanese vegetarian meals, teaching you a selection of rice and noodle dishes.</p>
</article>
</a>
<a href="sauces.html">
<article>
<figure>
<img src="images/teriyaki.jpg" alt="Teriyaki sauce" />
<figcaption>Teriyaki Sauce</figcaption>
</figure>
<hgroup>
<h2>Sauces Masterclass</h2>
<h3>One day workshop</h3>
</hgroup>
<p>An intensive one-day course looking at how to create the most delicious sauces for use in a range of Japanese cookery.</p>
</article>
</a>
</section>
<aside>
<section class="popular-recipes">
<h2>Popular Recipes</h2>
<a href="yakitori.png">Yakitori (grilled chicken)</a>
<a href="tsukune.png">Tsukune (minced chicken patties)</a>
<a href="okonomiyaki.png">Okonomiyaki (savory pancakes)</a>
<a href="mizutaki.png">Mizutaki (chicken stew)</a>
</section>
<section class="contact-details">
<h2>Contact</h2>
<p>Yoko's Kitchen
<br />
27 Redchurch Street
<br />
Shoreditch
<br />
London E2 7DP
</p>
</section>
</aside>
<footer>
© 2011 Yoko's Kitchen
</footer>
</div>
<!-- .wrapper -->
</body>
</html>
| Path Expression | Expression Result |
|---|---|
/html |
Select the root element catalog. Note: If the path starts with a slash ( / ) it always represents an absolute path to an element! Your absolute path is the same as your context in this case. |
//article |
Select all nodes with the name “article” |
//article/.. |
Selects all of the parents of the nodes with the name “article” |
/html/body/div/section/article/figure/img/@alt |
Select all img node alt attributes |
/section/* |
Select all the child element nodes of the section element |
//* |
Select all elements in the document |
//title[@*] |
Select all title elements which have at least one attribute of any kind |
//@* |
Select all attributes |
//@alt/.. |
For all nodes that have the alt attribute, select the immediate parent |
/html/body/div/aside/section[1] |
Select the first section element in /html/body/div/aside |
//*[@href] |
Select all elements with an href attribute |
/html/body/div/aside/section[@class="popular-recipes"] |
Select section element with the attribute “popular-recipes” in /html/body/div/aside |
//a[@class!="current"] |
bring back all a elements where they have a class attribute but it isn’t current |
//a[not(@class="current")] |
bring back all a elements except the ones that have a class attribute equal to current (Note: they do not need to have a class attribute) |
/descendant::h3 |
Select all h3 element nodes |
//attribute::alt |
Select all alt attribute nodes |
//body/div/section/following-sibling::* |
Select all elements to the right (subsequent to) //body/div/section |